The importance of having a high level of cyber resilience is increasing exponentially these days as cyberattacks become more complex and frequent. Cyber resilience is the ability of a company to maintain business operations in the event of a cyberattack and to return to normal state as quickly as possible. This requires both preventive measures to avoid cyberattacks and strategies for rapid response and recovery in the event of a successful attack.
A key pillar of cyber resilience is effective incident response. Incident response involves responding quickly and in a systematic manner to security incidents, identifying their causes, and taking the necessary steps to limit the damage and restore affected systems and data.
If you wish to evaluate and improve your organization’s incident response processes, an Incident Response Readiness Assessment might be a suitable option. Such an assessment is useful for evaluating measures already in place, identifying potential weaknesses, and ensuring that your company is well prepared for security incidents.
Table of contents
What Is Incident Response Readiness?
Incident response readiness describes the level of preparation of a company and its ability to efficiently detect, investigate and respond to security incidents. This includes the detection of cyberattacks using monitoring systems, the detailed analysis and reconstruction of incidents, and the rapid and effective response to limit damage. It also comprises measures to restore affected systems and data as well as preventive measures to avoid future incidents. Thorough process-related, strategic and technical preparation is essential for achieving a high level of incident response readiness.
Process-Related Preparation
Process-related preparation refers to the operational procedures and workflows that will be applied in the event of a security incident. In this step, strategies for dealing with various scenarios such as ransomware attacks, data leaks or distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks are to be developed and defined. This includes creating detailed step-by-step plans for a quick and efficient response to incidents, e.g. playbooks or checklists, defining responsibilities, assigning tasks, and documenting the processes for managing incidents, crisis communication and the documentation of incidents. Useful resources for communication during a cyberattack can be found at CERT-NZ and BACS.
Strategic Preparation
Strategic preparation refers to the long-term planning and integration of incident response into the organization’s overall security strategy. This includes the development of comprehensive security policies and the continuous review and adaptation of the security strategy to new threats. In addition, strategic preparation involves raising awareness among employees, training as well as regular exercises and simulations to test the effectiveness of incident response plans and ensure that everyone involved knows what to do in the event of an emergency.
Technical Preparation
Technical preparation focuses on the technical infrastructure and its maintenance. This step covers the creation and maintenance of a network plan, a complete asset inventory, patch and vulnerability management, and the implementation of monitoring systems and security audits at regular intervals.
The overall goal of each step of preparation is to improve your organization’s resilience to cyberattacks and ensure that your company can respond quickly and effectively in the event of an incident.
What Is an Incident Response Readiness Assessment?
An Incident Response Readiness Assessment is a systematic evaluation process designed to determine your organization’s level of incident response readiness, i.e. how well your organization is prepared to respond to cyber incidents. The assessment usually includes a review of policies, procedures, technologies and resources required for incident management, analysis, and recovery of critical systems and data following a security incident. The goal of the assessment is to identify gaps in the security strategy and provide recommendations on how to close those gaps to increase and improve cyber resilience and incident response readiness.
What Is the Incident Response Readiness Assessment Based on?
The assessment is based on the following norms and standards:
- NIST SP 800-53 Rev.5: comprehensive security and privacy controls
- ISO/IEC 27001:2022: requirements for an information security management system (ISMS)
- ISO/IEC 27002:2022: practical recommendations for security controls
- ISO/IEC 27035-1:2023: principles of incident management
- BSI IT-Grundschutz Compendium: established methods for securing IT systems
- BSI Standard 200-2: standard for information security management
- BSI Standard 200-4: standard for business continuity management
These norms and standards provide best practices and guidelines on how to improve information security, risk management and incident response readiness. They are an essential part of the assessment, as they help to enhance security practices, ensure compliance and establish a solid security management system.
What Does the Assessment Cover?
A structured assessment grid (see Figure below) is used for the Incident Response Readiness Assessment.
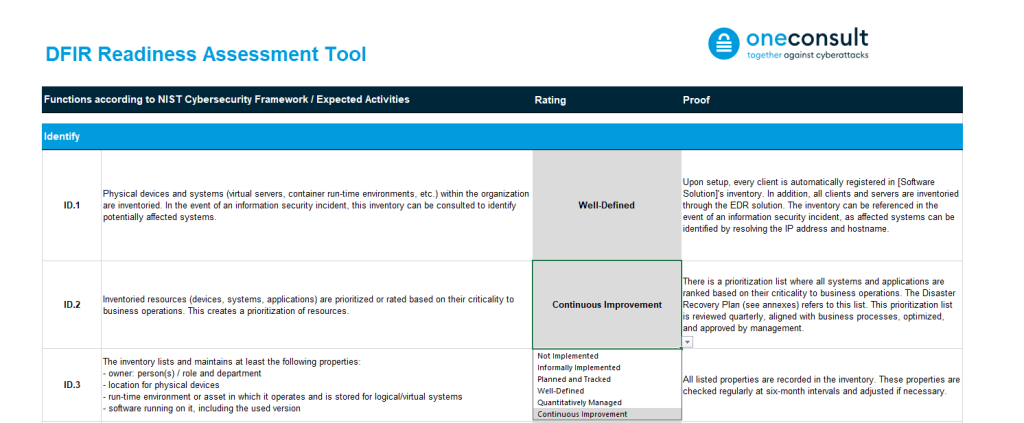
The grid consists of a set of audit criteria to be checked; they are divided into six sections that cover different topics of incident response readiness. These sections are based on the functions of the NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) Cybersecurity Framework (version 1.1) and are complemented by subject-specific questions that specifically assess the degree of fulfillment of the organization’s incident response readiness. The six sections are listed below, each with an example of an audit criterion.
- Identify (ID): The “Identify” section covers the identification and documentation of assets and resources that are important for the organization’s information security. This also includes the definition and establishment of a well-developed emergency organization that supports decision-making and the containment of infections in the event of an incident.
Example of audit criteria: Inventoried resources (devices, systems, applications) are prioritized or rated based on their criticality to business operations. This creates a prioritization of resources. (ID.2 - Protect (PR): “Protect” refers to the implementation of security measures to minimize the risk of successful cyberattacks; such security measures may include multi-factor authentication (MFA), endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, and regular training and exercises for employees and decision-makers.
Example of audit criteria: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is enforced for all systems and applications directly accessible from the internet, as well as the user accounts associated with them. (PR.1) - Detect (DE): This section is about identifying anomalies or suspicious activity through monitoring and protection systems. This also includes centralized and tamper-proof storage of logs and regular vulnerability scans.
Example of audit criteria: A reporting point exists through which information security incidents can be reported. (DE.3) - Respond (RS): Planning and implementing measures to manage information security incidents is of central importance here. This includes an incident response plan that addresses various matters, such as roles, responsibilities, processes and communication policies.
Example of audit criteria: The incident response plan is executed and followed in case of an information security incident. (RS.3) - Recover (RC): This section focuses on the recovery of systems and data following an information security incident, including regular backups and clearly defined recovery strategies.
Example of audit criteria: Backups are performed at defined, regular intervals and checked for errors, completeness, and correctness. (RC.1) - Learn Lessons (LL): “Learn Lessons” is about continuously improving processes based on experience and lessons learned from past incidents
Example of audit criteria: Lessons learned from information security incidents and associated vulnerabilities and threats are identified, documented, and communicated. (LL.2)
This comprehensive assessment ensures that the organization’s incident readiness measures are both reliable and effective.
How the Incident Response Readiness Assessment Works
The first step in the Incident Response Readiness Assessment is a self-assessment completed by the customer using the structured assessment grid described above. The customer goes through all the audit criteria and determines the maturity level (see Maturity Rating) at which they consider their company to be for each criterion.
The self-assessment is verified and complemented by Oneconsult’s analysis of existing documents and interviews with key persons in the company. Based on the information gathered, Oneconsult prepares an assessment and a report with customized measures and recommendations. This holistic approach ensures that all relevant aspects are taken into account and that the suggested measures are precisely tailored to the company’s needs.
Maturity Rating
The maturity levels in the assessment are applied using a predefined rating scale. This scale is based on the Security & Privacy Capability Maturity Model (SP-CMM). The SP-CMM is a model designed to help organizations to evaluate and improve their security and data privacy measures. It was chosen as the foundation for the scale because it provides an established framework for systematically measuring and continuously improving the maturity of security and data privacy measures. The audit criteria are each rated on a scale of 0 to 5; the maturity levels are defined as follows:
- 0 – Not Implemented: Requirements are not met, no measures to achieve objectives
- 1 – Informally Implemented: Objectives are known, but measures are reactive and informal
- 2 – Planned and Tracked: Formal measures have been taken, but there are still gaps
- 3 – Well-Defined: Measures are standardized and coordinated, results are documented
- 4 – Quantitatively Managed: Measures are controlled and regularly evaluated
- 5 – Continuous Improvement: Measures are continuously reviewed and optimized
The following spider chart shows how the results of the assessment are visualized; the chart contains the maturity levels and different sections:
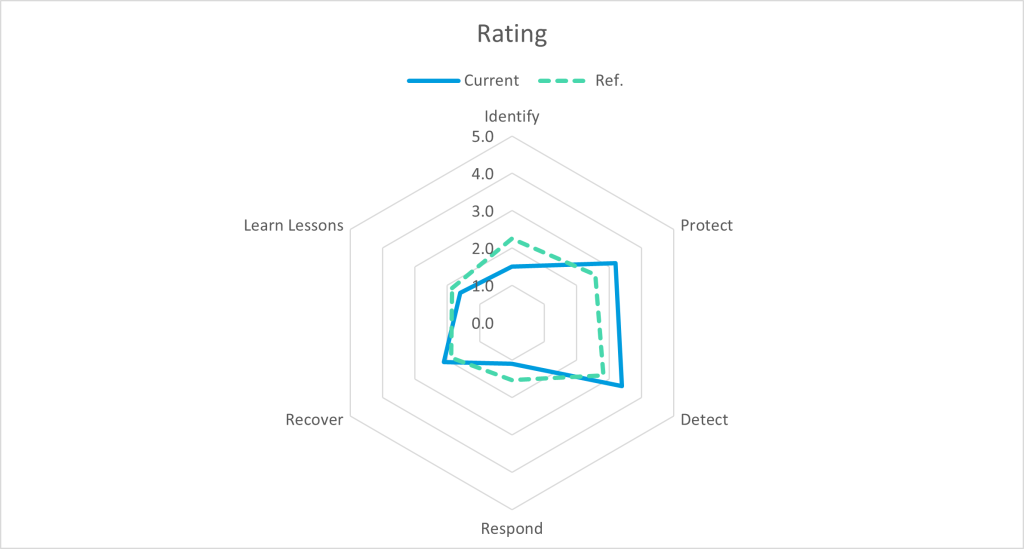
Using the results of the Incident Response Readiness Assessment, companies can compare themselves with other organizations that have already carried out such an assessment. In particular, companies in the same industry provide valuable comparisons as industry-specific benchmarks are used. This enables organizations to better assess their own security level and identify areas for improvement.
In this example, the maturity level of the organization’s incident response readiness in certain areas, such as “Protect (PR)” and “Detect (DE)”, may be well above the cross-industry reference (Ref), while there is room for improvement in other areas, such as “Respond (RS)” and “Identify (ID)”.
Benefits of the Incident Response Readiness Assessment
In summary, there are many benefits to conducting an Incident Response Readiness Assessment:
- The assessment provides an in-depth and thorough review of your organization’s existing security measures and gaps, allowing you to identify potential risks at an early stage.
- Assessing your organization’s incident response readiness against a structured model to evaluate maturity levels shows how well prepared your organization is to detect, investigate, and respond to security incidents.
- Based on the results of the assessment, you will receive specific and customizable recommendations tailored to your organization’s needs and requirements to improve your security strategy.
- Implementing the recommended measures enhances your organization’s ability to defend against cyberattacks, respond to incidents and recover quickly, which strengthens overall security and resilience.
- Industry-specific benchmarks allow you to compare your organization with others that have completed a similar assessment. This allows you to better assess your own level of security and identify areas for improvement.
Why Should You Conduct an Incident Response Readiness Assessment?
An Incident Response Readiness Assessment provides a comprehensive evaluation and customized improvement plans that are based on well-established standards and extensive experience. Since the assessment requires key members of your organization to actively participate and provide accurate information, you get a credible and effective assessment that leads to actionable insights and better incident response readiness.
Invest in your cyber resilience with an Incident Response Readiness Assessment and ensure you are well prepared for future security incidents. Contact an expert to learn more about how you can strengthen your cybersecurity measures.



