In the digital world, companies are constantly exposed to new threats. Phishing attacks are among the most insidious forms of such threats, as what looks like a simple click on an email can have devastating consequences – from financial loss to data breach.
But what exactly does “phishing” mean? What methods do cybercriminals use to steal confidential information? And above all: How can companies effectively raise their employees’ awareness and respond correctly in an emergency?
In this blog post, we’ll show you why awareness and training are so important and give you valuable tips on how you can protect your company from the growing threat of phishing.
Table of contents
What Is Phishing?
Phishing is a fraudulent technique in which the attackers pretend to be legitimate senders in order to obtain confidential data such as login credentials, credit card details or company information. The term “phishing” is a combination of the words “password harvesting” and “fishing”, which symbolizes the method of fishing for information.
This type of scam involves sending fake emails or messages pretending to come from legitimate organizations or individuals. It is a form of social engineering. The messages trick recipients into clicking on manipulated links or scanning a QR code, for example (see screenshot).

From the attackers’ point of view, the messages are supposed to persuade the recipients to share sensitive data or enter it on fake websites. Their goal is to gain direct access to important accounts or to install malware.
Besides fake websites and emails, phone calls (vishing) or text messages (smishing) can also be used to for phishing attacks, which can be extremely convincing. The consequences of such attacks are far-reaching and include financial loss, identity theft and serious security breaches in companies. Phishing can serve as a gateway to other cyberattacks, such as criminals infiltrating company systems to steal data or spread ransomware, which in turn leads to the encryption of data and ransom demands.
What Are the Different Types of Phishing?
Phishing methods vary greatly in the way they are carried out and range from large-scale campaigns to targeted attacks on individuals. Understanding these methods in detail is essential for effective protection. There are the following four types of phishing:
Spear phishing is targeted at specific individuals, organizations or companies. Cybercriminals gather detailed information about their targets to create customized and persuasive messages. They aim to steal sensitive data or gain access to protected networks. You can find more detailed information on spear phishing attacks in our blog article “What Is a Spear Phishing Attack?”.
Whaling, also known as “whale phishing”, focuses on high-level executives of a company who are targeted because they have access to particularly sensitive information. To circumvent the generally high security precautions of such targets, attackers use sophisticated techniques.
Smishing, or SMS-based phishing, is the practice of sending text messages with malicious links or requests to disclose personal data. This is often done under the guise of tempting offers that appear to come from trusted sources.
Vishing, also known as voice phishing, uses phone calls to obtain personal or financial information. The attackers create an atmosphere of urgency and authenticity in order to persuade victims to disclose sensitive data.
9 Characteristics of Phishing Messages
Although phishing attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, there are some distinctive characteristics of phishing that will help you identify such a scam and protect yourself from account compromise, data loss or other security risks.
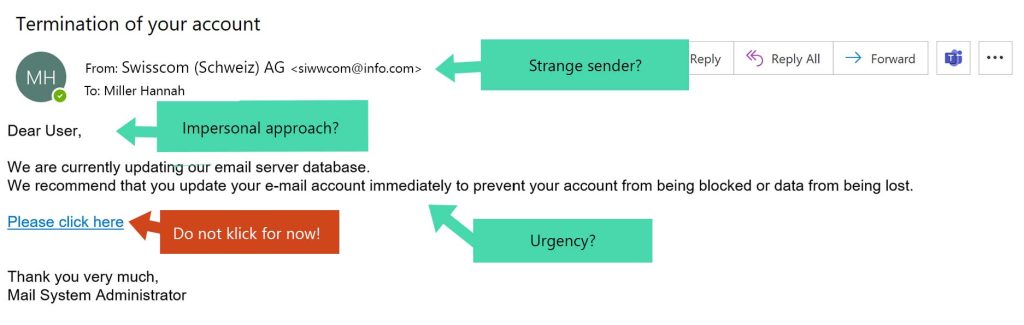
- Unusual senders: Caution is advised when you receive messages from unknown senders; but even contacts you are familiar with may have been compromised and consequently misused for phishing.
- Urgency: Phishing attempts often create a sense of urgency to tempt you to take rash action. Be suspicious of messages with tight deadlines.
- Suspicious links and attachments: Do not click on links or open attachments that appear suspicious, especially if the message comes from a sender you do not know. You can hover the cursor over links without clicking on them to see the actual URL in the preview. This helps you to determine whether the link leads to a suspicious website. Also be careful with PDF attachments. Only open them if you receive them from a trusted source. There are tools and techniques that allow you to check PDF files for malicious content before you open them.
- Request to disclose sensitive data: Do not trust requests for personal or financial information. Official institutions rarely use emails to ask for such data.
- Generic forms of address: Impersonal or general forms of address can be an indication of phishing.
- Spelling mistakes and unusual wording: Spelling and grammatical errors or a strange writing style are also red flags.
- Messages in foreign languages: Be alert if you receive unexpected messages in a language that is unusual for the sender.
- Logic errors in the communication: Implausible requests or unexpected messages from people and companies that you are not currently in contact with are suspicious.
- Discrepancies in the sender’s email address: Check the sender’s email address carefully. Even if the name seems familiar, a different email address may indicate that it is a fraud attempt.
Phishing emails can even use personal forms of address, imitate known logos and mimic the writing style of real communication. This makes it all the more important to check not only the content, but also the context, the technical structure and the plausibility of the request. When in doubt, it is advisable to contact the person or company in question through another known communication channel to confirm the legitimacy of the message.
Below you can see an infographic that shows the most important characteristics of phishing messages:
How to Protect Your Company Against Phishing Attacks
In order to effectively protect your company from phishing, it is crucial to take certain security measures and maintain a high level of awareness. The following guidelines and tips will help your company and your employees to stay secure.
- Check the URL: Make sure that the web addresses are authentic. Save log-in pages you frequently use as bookmarks and avoid clicking on links in suspicious emails. If possible, services should be accessed directly via the official website.
- Be careful about personal data: Sensitive information such as passwords or credit card details should never be passed on by email. If in doubt, it is more secure to contact the sender directly.
- Be cautious with downloads and attachments: Avoid clicking on download links and do not open any attachments from unknown or suspicious emails to minimize the risk of malware infection.
- Maintain an adequate level of skepticism: Be particularly cautious with unexpected emails, especially if they ask you to enter personal information.
- Use two-factor authentication (2FA): Enabling 2FA provides additional protection for your accounts.
- Verify the caller’s identity for requests via phone: Be wary of vishing calls and check the identity of the caller before disclosing any personal information. Suspicious calls should be ended immediately.
- Define a process for reporting suspicious emails: Set up a central point of contact for reporting and, if possible, integrate a phishing report button in email programs such as Outlook. This enables employees to report suspicious emails quickly and efficiently.
- Implement blocklists for malicious URLs: Use security feeds such as Feodo Tracker and ThreatFox to integrate them into your network gateways (proxy, firewall, etc.). This helps to block access to known malicious URLs and protect your network.
- Block dangerous file extensions: Certain file extensions are often associated with malware. Configure your email gateways to automatically block attachments with such extensions.
- Keep your software up to date: Regular updates of your software and operating systems are essential. Such updates close security vulnerabilities and reduce the risk of vulnerabilities being exploited. Using antivirus programs and firewalls further strengthens your protection against malware.
- Optimize your spam filter and flag external emails: By customizing your spam filter, phishing attempts and unwanted emails can be filtered more effectively. Flagging emails from outside your company as “external” raises employee awareness and increases vigilance against potential threats.
Implementing the above measures, along with continuously training your employees and raising their awareness, will strengthen your company’s defenses against phishing. Investing in cybersecurity awareness is essential to prepare your team to detect and defend against phishing attacks and other cyber threats. A proactive approach to cyber security keeps your company secure and competitive.
Emergency Measures in the Event of a Phishing Attack
If you discover that you have fallen victim to a phishing attack, you must immediately take targeted measures to minimize the damage.
- Identify the affected users: Immediately determine which users are affected. This is critical to understanding the scope of the attack.
- Check for other affected users in the company: Check whether the phishing email has been sent to other people in the company. If so, these emails should be deleted immediately to prevent further interaction.
- Analyze actions carried out: Clarify whether and which actions have already been carried out, e.g. clicking on links, opening attachments, entering login credentials, etc.
- Reset passwords and take security measures: Depending on the actions taken, passwords should be reset immediately, all active sessions terminated (wait at least one hour), multi-factor authentication (MFA) reset and a security scan performed on the systems.
- Evaluate the impact of the phishing attack: Determine the impact of the phishing attack, such as financial damage or loss of sensitive data.
- Inform the relevant parties: Based on the impact determined, relevant parties should be informed, e.g. banks, customers and other stakeholders, especially if their data has been compromised.
- Escalate the incident: In the event that an account or system has been compromised, you should escalate an incident to your internal security office or external partners for specialized support.
- Isolate affected systems: If systems have been infected with malware, isolate them immediately to prevent malware from spreading further.
- Communicate internally: Inform your employees about the incident and the measures taken to raise awareness of the threat and promote further preventive measures.
- Contact service providers: If necessary, inform your IT service provider to increase the security of your data and systems and work closely with your financial institutions to block or monitor access.
- Report the incident: Report the incident to the Federal Office for Information Security in Germany or the National Cyber Security Centre NCSC in Switzerland.
Taking these steps will help you to ensure an appropriate response in the event of an emergency and limit the impact of a phishing attack. At the same time, you should continuously raise awareness and train your employees in order to further strengthen your company’s resilience to threats. A proactive security strategy, alongside regular system updates and ongoing cybersecurity training, is crucial to protect your company in the long run.
Conclusion
Phishing is a complex and persistent threat that affects companies of all sizes and industries. The key to effective protection is a thorough understanding of phishing, the ability to recognize it and effective countermeasures. It is important to know how to identify phishing attempts based on their characteristics. In addition to that, companies should regularly carry out security updates, use two-factor authentication, protect sensitive data and promote a culture of awareness.
If a phishing attack has already occurred, it is essential to respond quickly and take measures such as identifying affected users and resetting passwords. Reporting the incident supports the recovery of security.
Continuous training promotes your employees’ cyber security skills and an effective incident response plan ensures a rapid response in the event of an emergency. To further enhance your security, we offer customized services. Our Incident Response Retainer provides you with immediate support in the event of a cyberattack to minimize damage, while our Cyber Security Academy helps to raise cyber security awareness among your employees through targeted training, making them the most important line of defense against attacks.



